Wednesday, January 20, 2021 was the start of a new era in American politics. Joseph Biden was inaugurated as the 46th president of the United States. It ushered in a dramatic change in terms of leadership, but also represented the end of a four-year period of turmoil in the lives of everyday people, marked by division, dissent, violence, hatred, self-serving policies, incivility, nepotism, and greed. President Biden acknowledged the extraordinary times in which we live during his inaugural address. He named six distinct crises that the US faces: the coronavirus pandemic, climate change, growing inequality, racism, America’s global standing, and the general attack on truth and democracy.
“Any one of these will be enough to challenge us in profound ways. But the fact is, we face them all at once,” Biden said. “We will be judged–you and I–by how we resolve these cascading crises of our era.”
The Cascading Crises
Biden’s words were sobering because they put a lot of what challenges us onto one overwhelming list. By acknowledging the intimidating set of circumstances in which we find ourselves, we can clearly see what we’re up against as individuals and as communities. However, most of these issues have been with us for quite some time. While the global pandemic first originated just a year ago (in January 2020), the other issues stretch back for decades, even generations. It is hard to say which of the stated problems is the most pressing. It seems we must tackle them all simultaneously, probably in small increments, if we are to see progress. And while we might rely hopefully for solutions from our new government, the truth is that addressing every one of these six “cascading crises of our era” is going to begin at home, in the attitudes and lives of normal, run-of-the-mill people.
Existing Strain Exacerbated by a Pandemic
Is it any wonder, looking at that list of crises, that many of us feel despondent, hopeless, and riddled with anxiety? The world seems daunting right now and fraught with uncertainty. As humans, we may feel as if we have little power to affect change; we may even feel as if our reserves of strength are diminished or completely depleted after such a long struggle, especially during an unprecedented pandemic. There is no doubt that our children are suffering profound and unknowable anxieties and fears, too. Research tells us that the levels of trauma among ordinary people are at an all-time high.
The pandemic alone has left millions without jobs, sent billions into isolation, and forced nearly everyone on earth to suddenly grapple with the discomforting fact that we are all physically vulnerable to an unseen viral enemy. “The scale of this outbreak as a traumatic event is almost beyond comprehension,” said Yuval Neria, the director of trauma and post-traumatic stress disorder at the New York State Psychiatric Institute and a professor of psychology at Columbia University Medical Center. Neria says that the current health crisis can’t be compared to the shock of the 9/11 terrorist attacks or even the sweeping desolation of World War II, as the anxiety caused by those events was geographically limited. In this case, he said, “there are no boundaries.” We are experiencing truly global trauma.
Global Trauma
The most important first step is to recognize that we are all traumatized. To a greater or lesser or degree, every single person on the planet has suffered change or loss over the past year. Millions have lost their jobs – an economic disaster for some communities that disproportionately affects women, children, and minorities. 400,000 Coronavirus deaths in the United States alone means that millions of people are suffering profound grief over the loss of a loved one. The recent overt rise in white supremacy movements has left countless citizens of color living in fear in a country that proclaims equality as a core value. So, while all the normal sadness and losses of life are still routinely taking place, they are taking place against a never-before-seen backdrop of darkness, sadness, death, and uncertainty.
Perhaps there is comfort to be found in the fact that we are experiencing this simultaneously. While each person’s journey is unique, and so it’s not accurate to broadly claim that we are “all in this together”, nobody has been left unscathed by the recent stresses of life. It’s not worthwhile to compare your suffering to that of others, or to assume that people who seem to be coping better than you actually are. Because, in fact, our whole world has been traumatized. How can we know this? The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) is the agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services that leads public health efforts to advance the behavioral health of the nation. It provides three Es to ascertain the degree of trauma you’ve likely experienced based on your personal circumstances and natural coping abilities. By understanding how the three Es work together, you’ll better understand how we’ve been affected by the past few years and whether you will come out the other side of these challenges in a better place. The good news is that the power really does lie within you, as an individual, and you have some choice over where you end up, regardless of what happens.
The Three Es
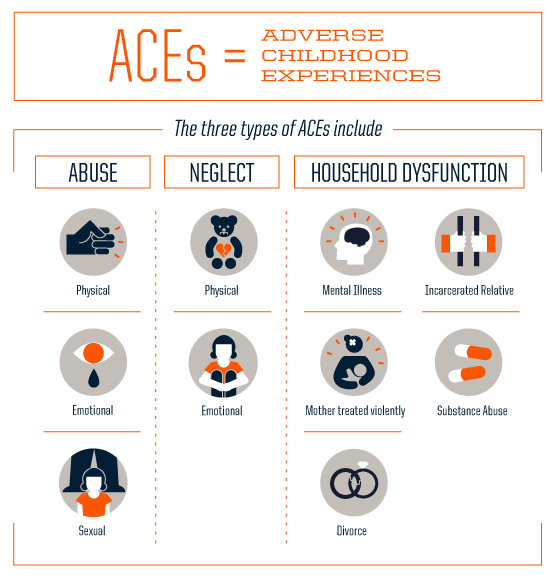
Event: This is a situation or experience that happens to a person or in their environment. The original Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) study conducted over twenty years ago looked at ten specific events in the lives of children under 18 that might result in trauma. These included incidents of abuse (physical, emotional, sexual), neglect, and household dysfunction. Since then, the idea of what other ACEs should be on the list has expanded greatly to include many other potentially traumatic events like bullying, extreme medical interventions, natural disasters, etc. Usually these events need to result in sustained toxic stress that interferes with a child’s natural, healthy development for them to be considered traumatic – but everyone is unique and even a single profoundly distressing event can be enough to cause long-lasting trauma.
Experience: An individual’s experience of a particular event or circumstance helps to determine whether that event qualifies as traumatic. What one person considers traumatic might feel very different to another. According to SAMHA, “it is how the individual labels, assigns meaning to, and is disrupted physically and psychologically by the event determines whether that event is traumatic.” Age old wisdom tells us that we have a little control over what happens to us. What we can control, however, is how we choose to respond to what happens to us. This is a very empowering approach. Resilience (which may have a genetic component, but which is also clearly a muscle that can be exercised) may determine our degree of “bounce” — that is, how readily and quickly we are able to recover from and address adversity.
Effects: The combination of the events and our experience of those events can have a long-lasting effect on our lives. These effects may occur immediately or have a delayed onset. Their duration may be short or long term. Throughout our study of ACEs, we have learned that, in the absence of positive buffering influences, children raised with high levels of adversity can suffer neurological and physiological development delays which disadvantage them mentally and physically for their whole lives. But a counteracting, positive influence can serve as the antidote to all that toxicity and studies show that it can take as little as one buffer to right the course for a child.
When we understand what trauma is, how it affects children and their development, and how all of us are suffering a great, big dose of potential trauma right now, we can begin to employ empathy in our approach to others. Only then can we begin to “be the change we wish to see in the world”.
Take Back Your Personal Power
So, given that most of us are not politicians with the power to make sweeping legislative changes, what can we do? The answer is to take a moment and reassess. Call on the wisdom of perspective. Nothing lasts forever and all of us have power. We never feel that power as strongly as when we make the conscious decision to take it back. As individuals, we each have strength — perhaps not to overcome overwhelming global issues but certainly to address them ourselves in small ways that can change our immediate communities.
Get Trauma-Informed
The first crucial step is to get trauma-informed. By simply reading this blog means you’ve made a start to learn a little about ACEs and trauma. Being trauma-informed is broadly defined as embracing practices that promote a culture of safety, empowerment, and healing, and that encourage support and treatment of the whole person rather than treatment of individual symptoms or specific behaviors. Trauma-informed care initially shifted the focus from: “What’s wrong with you?” to: “What happened to you?” This attitude shift illustrates a move away from identifying behaviors in the moment which seem negative and digging deeper to get at the root causes of those behaviors and so start to work on healing them.
Armed with a knowledge of the three Es and an understanding of the importance of being trauma-informed, it’s time to review the concept of global trauma and distill it down to our own lives. In the coming months, our blog will look at practical ways you can become more trauma-informed in your workplace, the organizations to which we belong, and in your own home.
For our part, at Center for Child Counseling, we’re mission-driven to support children and families experiencing trauma – which means our client base now includes everyone! We’re providing extensive community resources in the form of online trainings that deliver crucial information and offer coping skills to parents and teachers. Our website offers help with techniques to reduce stress and assist children to deal with their fears over the pandemic. We can also tailor-make trainings for your specific group or organization to address your questions and needs around ACEs or trauma.
We’re also fortunate to work in a larger community that’s committed to trauma-informed growth, too. In Palm Beach County, some major initiatives keep us focused on this goal. We partner with other stakeholder agencies on the Birth to 22 initiative where we serve on the Trauma Sensitive Community Committee which strives to build trauma-informed best practices and ACEs awareness.
How can you make a difference in your world? What will empower you to counteract the “cascading crises of our era”? Each of us needs to assess ourselves and where we are on the spectrum of mental health. We’ll be offering guidance and support for you and your children on this journey. We are all dealing with our own traumas but sometimes the solution lies within. If you need extra help, ask for it from those who care about you and reach out to mental health professionals for their assistance. If you have a day when you feel you have the inner reserves to give to others then reach out to them and offer your help and compassion. Bringing trauma into the light is one way of addressing it. As Dr. Martin Luther King (whose birthday was also celebrated this past week) famously said: “Darkness cannot drive out darkness; only light can do that…Hate cannot drive out hate; only love can do that.”
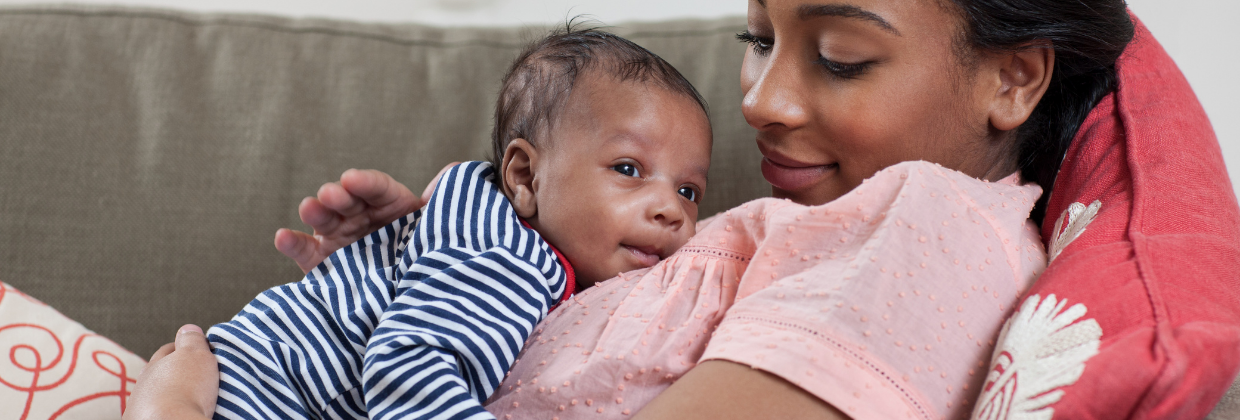
 Anyone who has looked into the eyes of a newborn baby knows from infancy, humans seek connection. We carry this need for connection throughout our lifetime, and from birth it provides the foundation for all relationships.
Anyone who has looked into the eyes of a newborn baby knows from infancy, humans seek connection. We carry this need for connection throughout our lifetime, and from birth it provides the foundation for all relationships. At the Center for Child Counseling, we focus on a public health approach to building awareness and action around addressing childhood adversity and trauma.
At the Center for Child Counseling, we focus on a public health approach to building awareness and action around addressing childhood adversity and trauma.
 Julie Fisher Cummings, Chair of the Board for the
Julie Fisher Cummings, Chair of the Board for the 
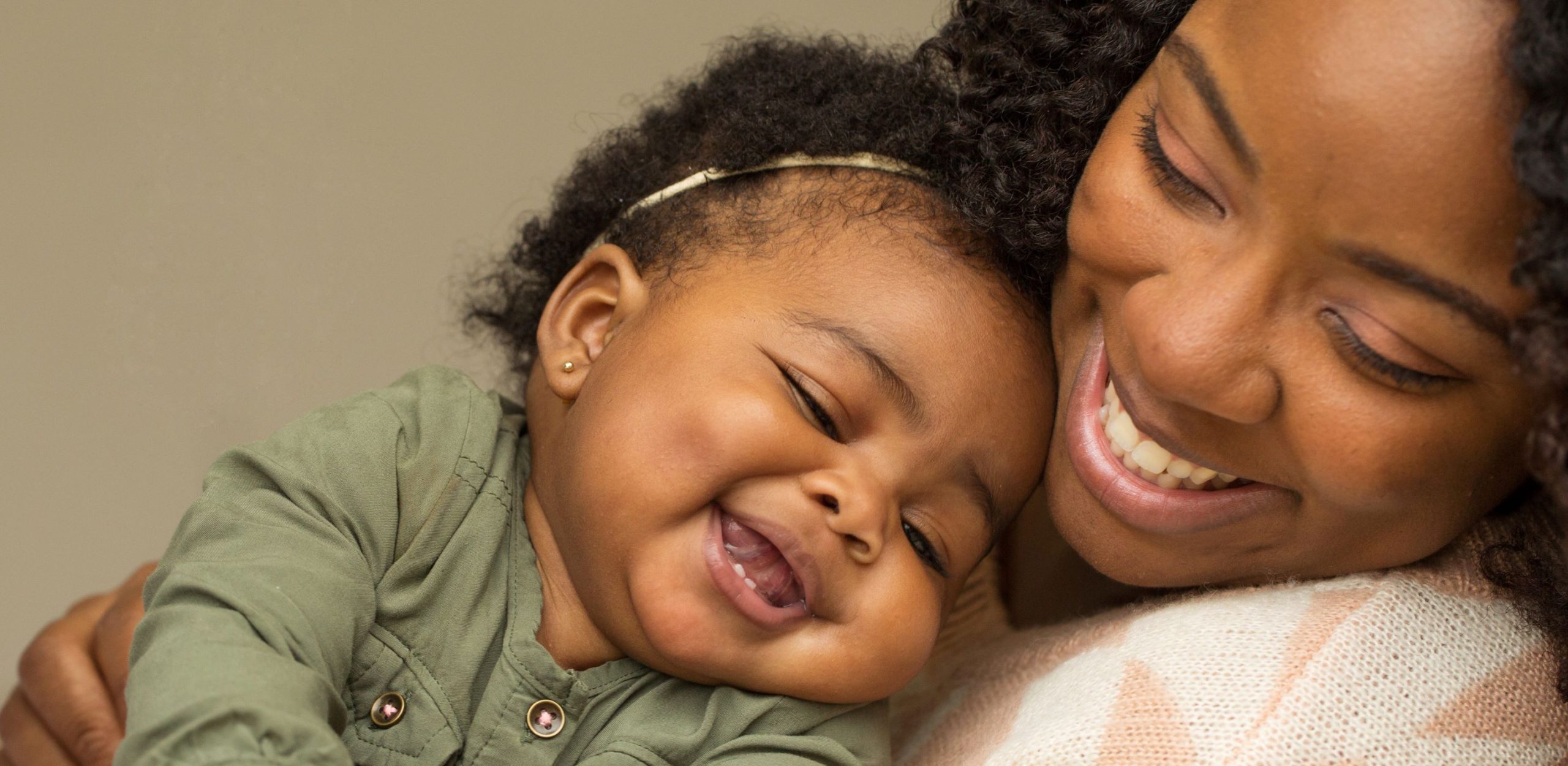



 Clearly, the negative consequences of poor attachment show up early and can last throughout the lifespan. So, where do Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) and attachment intersect? When we look at the original
Clearly, the negative consequences of poor attachment show up early and can last throughout the lifespan. So, where do Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) and attachment intersect? When we look at the original  Even when children have missed out on vital primary caregiver attachment during the formative years, simple connection can go a long way to help them catch up developmentally. The old African proverb: it takes a village to raise a child has never been truer. Positive adult interactions can
Even when children have missed out on vital primary caregiver attachment during the formative years, simple connection can go a long way to help them catch up developmentally. The old African proverb: it takes a village to raise a child has never been truer. Positive adult interactions can 


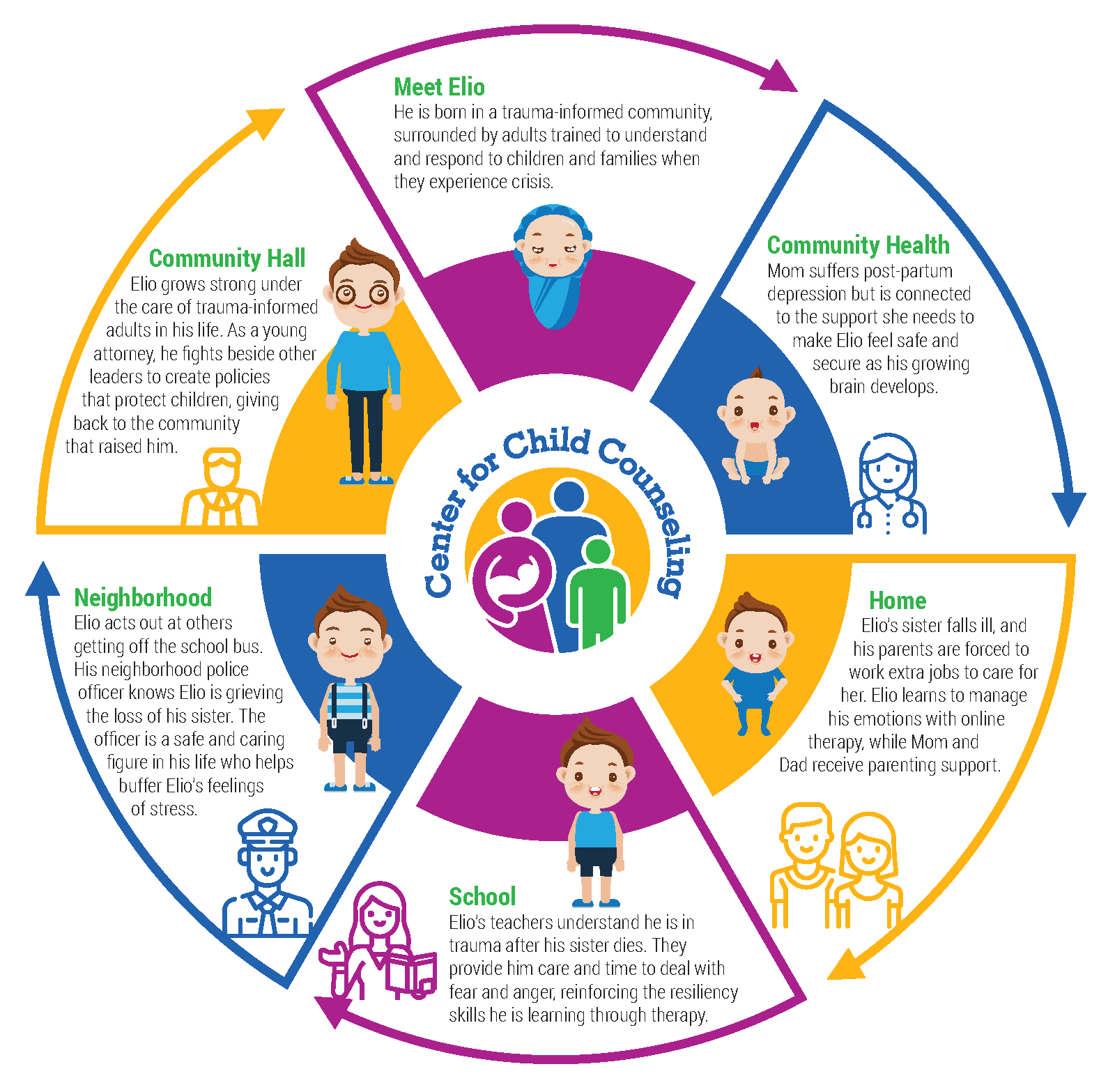 Our Role
Our Role