Stress is a strange thing. It’s both a feeling (a sense of being under intense pressure or emotional strain) and a mechanism by which the body’s systems respond to those feelings. We hear opposing statements about stress. Either stress is good for us because it motivates us to succeed, or all the stress in our lives in going to kill us… Which one is true? When it comes to stress, it’s a matter of degree. Yes, a little stress is part of human survival. It focuses us, energizes us, and helps us get things done. On the most primitive levels, feelings of danger trigger our body’s autonomic responses, flooding us with the hormones that once allowed us to flee from predators or enemies, or stand and fight them. Although that dramatic response is seldom needed these days, except in extreme cases of danger or sudden emergency, the stress response mechanism is still in place and vital in the rare instances when we need it. But this powerful system that’s built into every human body can be very dangerous—especially to children—when it’s triggered too frequently.
The body has several reactions to extreme danger or fear:
1.) It can embolden us to stand our ground and fight for our survival (FIGHT)
2.) It can trigger the strength and stamina we need to run away (FLIGHT)
3.) It can cause a state of near inertia in some people, thus the phrase “paralyzed with fear” (FREEZE)
It’s often hard to predict which response we’ll have in any given situation. In many cases, it seems that our body innately chooses for us but, in every case, the presence of danger sets off a series of chemical reactions in the body led by the brain and the endocrine (or glands and hormones) system.
The Immediate Effects of Adrenaline and Cortisol
The presence of danger or even severe unpredictability causes the brain to send a message to the glands to release adrenaline and cortisol. Between them, these two hormones do quite a lot to the body in a very short time:
1.) They increase the heart rate which raises blood pressure
2.) They expand the air passages to the lungs, bringing more oxygen to the body
3.) They rush sugar to the bloodstream
4.) They dilate the pupils of the eyes
5.) They prioritize the sharing of oxygen with muscles to give us power we may not know we had. Think about those news stories where people suddenly display incredible strength to save others, by lifting up a wrecked car to save a child, for example. Thank you, adrenaline!
However, adrenaline and cortisol are emergency measures — the last resort response for extreme situations. You might feel exhausted or quite nauseous after an extreme adrenaline dump, for example. That’s because your body is recovering from the intense activation and takes some time to manage and re-balance all the hormones in the blood. The body is always looking for homeostasis, or balance, where all systems are operating normally. Spikes of adrenaline and cortisol severely disrupt homeostasis and that’s a problem.
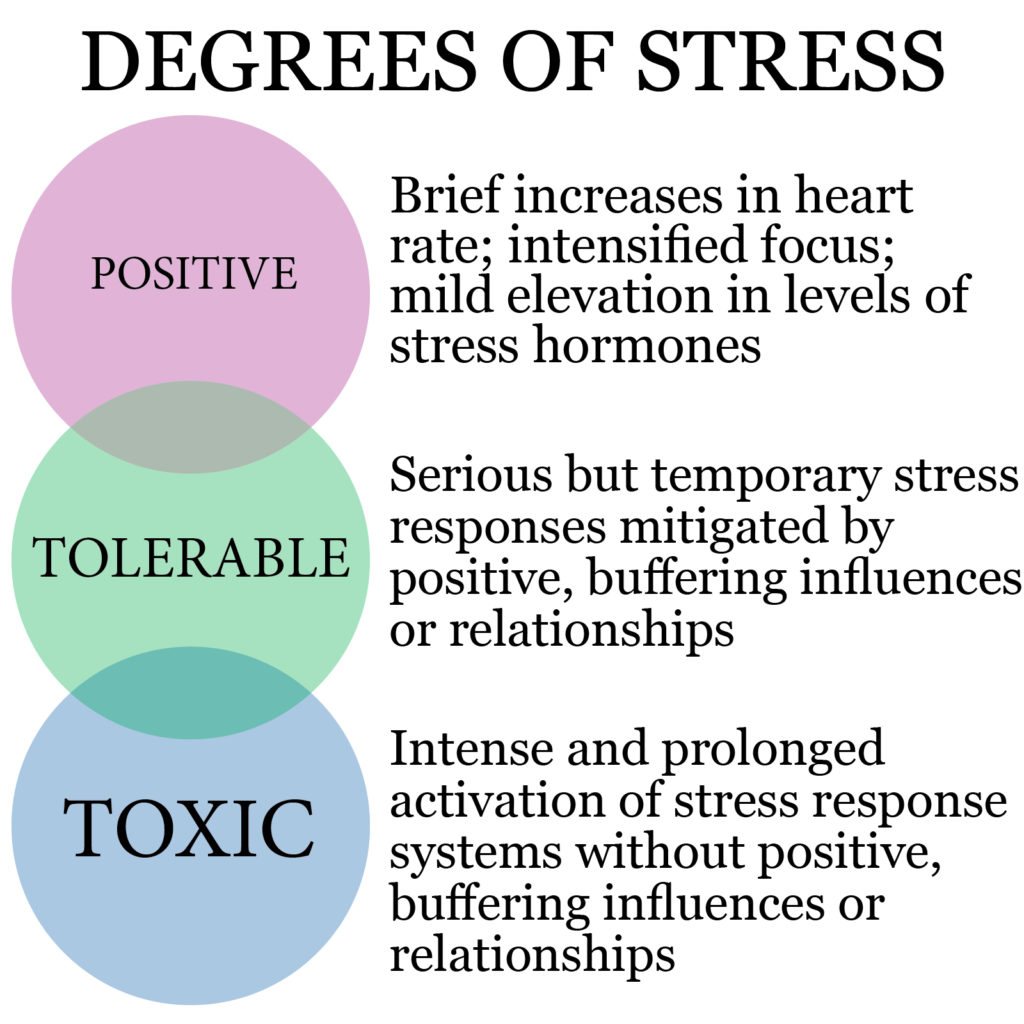
It’s true that there are good levels of stress. These are short periods of pressure that push us to complete tasks or focus on something we need to achieve. The stress passes and the body recovers quickly. However, when the stress is prolonged or repeated and there aren’t enough positive resources to counteract their effects, stress becomes dangerous and we call that toxic stress.
ACEs and Hormones
So why all this information on hormones and toxic stress? And how does it all tie back to understanding Adverse Childhood Experiences? Dr. Nadine Burke Harris, a pioneer in ACEs research, explains that adrenaline and cortisol are great if you encounter a bear in the woods. “The problem,” she says, “is what happens when the bear comes home single night?”
Continuous and repeated activation of the fight or flight response can “burn out” the system which is not intended to be in constant use. Adults suffer physical health issues if adrenaline and cortisol are released too frequently into their bodies. High blood pressure, chronic inflammation, high glucose levels, and low bone density are just a few of the numerous side effects which can result in:
• Anxiety
• Depression
• Digestive problems
• Headaches
• Heart disease
• Sleep problems
• Weight gain
• Memory and concentration impairment
The Effects on Children
For children, the situation is even worse. When little human brains and bodies are growing, there is a lot to do. The brain is developing at its fastest rate. Brain growth surges for the first 3 years of life, expands rapidly for the next ten years, then plateaus in the early 20s. But during the formative years, the body is using resources like the energy from food to accomplish countless tasks – building muscle, growing bone, honing the senses, and developing coordination and communication skills. With only a finite number of resources available, the brain allocates them to the most immediate and vital needs. In the case of constant fear and danger, the adrenaline process is triggered again and again at the expense of developing other parts of the brain and body.
Since survival must come first, that’s where all the energy goes, neglecting cognitive development and impeding those sectors of the brain vital for reasoning, self-regulation, and ultimately behavior and learning ability for the rest of a child’s life. In many cases, the lost ground is difficult, if not impossible, to make up.
A Life of Fear
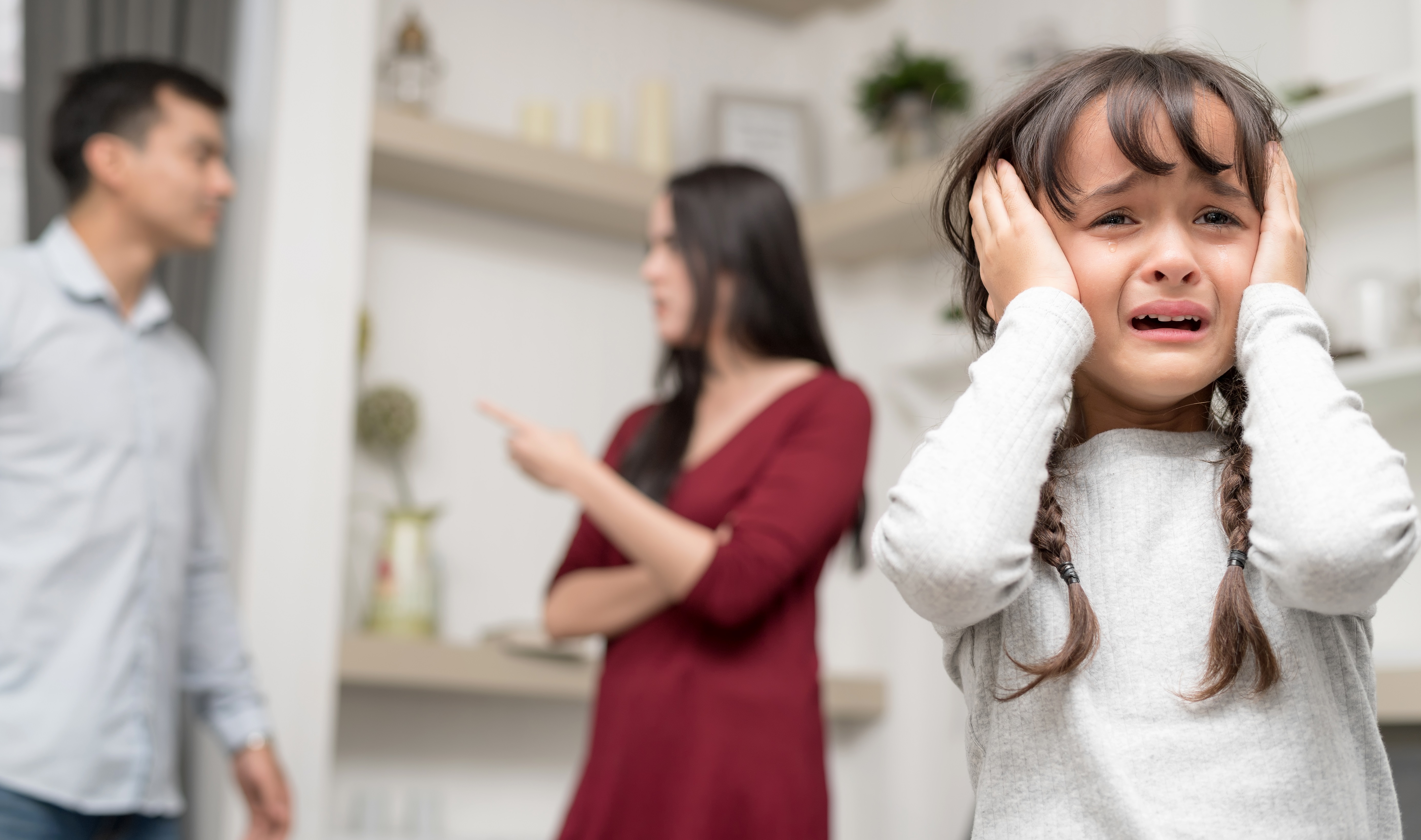
So, imagine a child living in a home with domestic violence. He lives with daily uncertainty and apprehension. He is on constant alert, waiting for the next tragic event. He is always in fear of witnessing or being the victim of abuse. When it occurs, he suffers extreme terror and a sense of helplessness. He lives his life in a constant state of toxic stress. The healthy development we owe all children has, in a sense, been stolen from him.
Effects of Toxic Stress on the Body Systems of a Child
Nervous System:
Toxic stress disrupts the developing brain, including changes to the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and amygdala. This raises the risk of cognitive impairment, learning disabilities, hyperactivity, poor self-regulation, inhibited memory and attention span, and anxiety.
Cardiovascular System:
Toxic stress increases a child’s risk of developing high blood pressure later in life because it elevates levels of inflammation that can damage the arteries. This can lead to heart disease, stroke, and other serious heart issues.
Immune System:
Toxic stress raises the risk of infections and autoimmune diseases due to chronic inflammation and other factors. This can impair the normal development of the body’s immune system.
Endocrine System:
Toxic stress can inhibit the functioning of hormones that regulate growth and development. It can also lead to obesity and impede or accelerate the onset of puberty.
This is what toxic stress looks like: It’s the relentless fear, anxiety, uncertainty, and terror that can cripple a child’s developing brain and body.
ACEs are not just experiences, they are events that cause chemical disruption in the body and result in lifelong mental and physical health issues. When a child is traumatized, abused, or neglected, we are changing who they are at a cellular level and causing damage from which it is very difficult to recover.
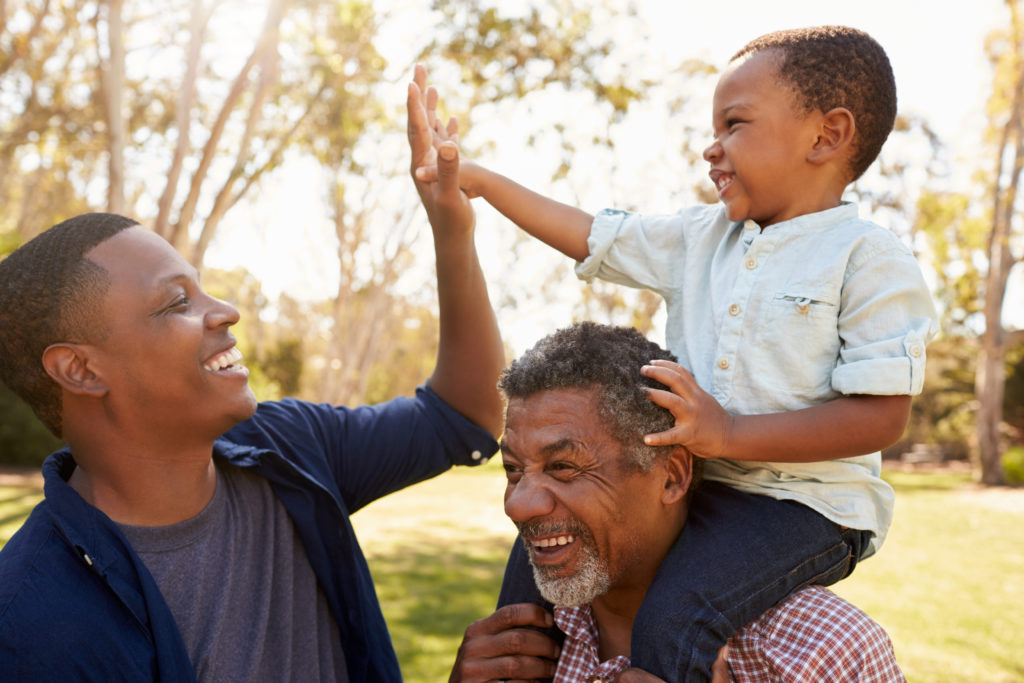
But hormones are powerful agents for good, too. A few months ago, this blog series focused on resilience and how to be a buffer for a child. Science shows that the presence of just one positive adult influence in a child’s life can help mitigate against the detrimental effects of ACEs. How does that work on a cellular level?
The Science of Kindness
As well as hormones that protect us, we have hormones that keep us close as a society. Human beings are communal creatures and we’ve developed to co-operate and help one another. Our bodies are even programmed to want to do this because it facilitates our survival imperative: we are stronger together than we are alone.
Acts of kindness often bring us a good, warm feeling. That’s not just an emotion, it’s a chemical reaction in the body. Kindness or altruism releases a chemical in our blood called oxytocin which sends positive, self-affirming signals to our brain. It’s often called the happiness drug. Oxytocin, along with dopamine and serotonin, make up what’s called the Happiness Trifecta. They increase the production of neurochemicals that lift your mood.
Kindness, care, support, warmth, compassion, and love all release these amazing chemicals which have positive health effects like lowered blood pressure, which reduces strain on the veins and arteries and can help stave off heart disease. These positive chemicals are fast-acting, too. In fact, chemicals resulting from a kind or loving interaction can positively influence the brain in as little as 3 seconds!
Remember a time when you felt anxious or depressed. Think how good a simple hug from a loved one felt at that time. That’s oxytocin! There’s a reason it’s called the “cuddle hormone”. Think about how uplifting an unexpected compliment can feel. That’s dopamine! The Happiness Trifecta help both the giver and the receiver to raise their levels of good, happy hormones. And its these hormones that counteract and neutralize the effects of adrenaline and cortisol.
Every time you have an interaction with a child that’s focused on giving something positive to them–even if it’s a high-five, a thumbs up or a big smile–that’s medicine that works as an antidote to ACEs. It hardly seems possible that it’s also doing great things for your own body, too.

Sign up now for news, events, and education about Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) and promoting resilience.
By submitting this form, you are consenting to receive emails from: Center for Child Counseling, 8895 N. Military Trail, Palm Beach Gardens, FL, 33410. You can revoke your consent to receive emails at any time by using the SafeUnsubscribe® link, found at the bottom of every email.